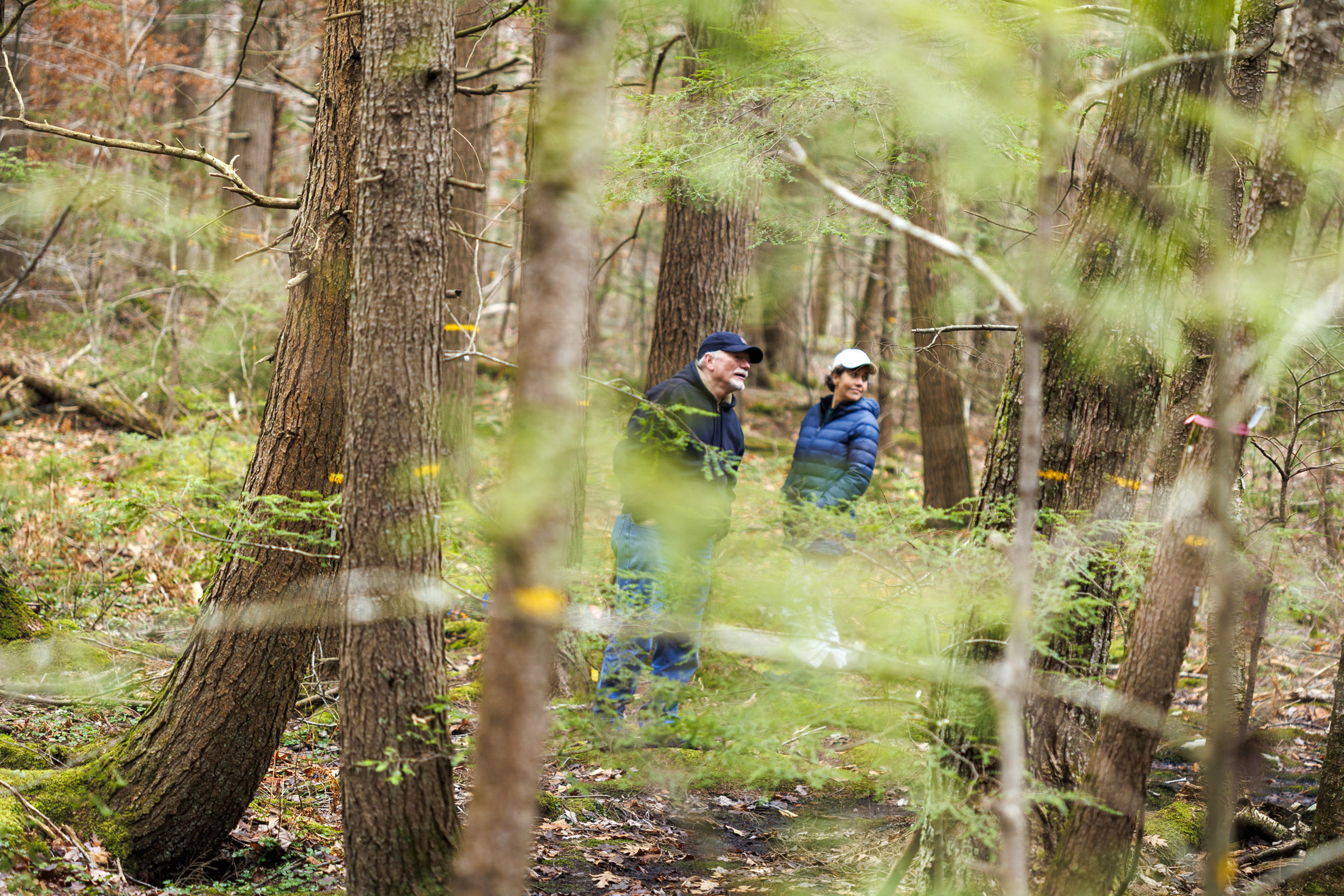
At Harvard Forest, climate change isn’t just an academic concept; it’s a vivid, daily reality that shape-shifts right before the eyes of researchers and ecologists. Senior investigator Emery Boose and Director of Outreach & Education Clarisse Hart are at the forefront of Harvard Forest research, studying the profound impact of climate change on the forest’s fragile ecosystem. Here, they observe not only a notable tree species shift, with new birch populations emerging but also the stress caused by invasive pests like the woolly adelgid. As global temperatures rise, the once lush canopy that characterized this 4,000-acre expanse now allows more light to penetrate, changing the forest floor’s dynamics. These observations highlight the urgent need to understand how ecosystems can adapt and demonstrate resilience in the face of unprecedented environmental change.
In the heart of Massachusetts, the 4,000-acre expanse of Harvard Forest serves as an insightful laboratory for investigating global warming phenomena. Scholars and scientists are focused on the ecological transformations driven by climate variances, including the ongoing alterations to local flora and fauna. One pressing concern is the rise of pest infestations, particularly by invasive species that disrupt established habitats. Alongside this, the gradual transition of tree demographics signals a critical shift that could redefine forest composition. Such studies extend our understanding of biological interactions and underscore the importance of fostering strong, adaptable ecosystems amid evolving climatic challenges.
The Role of Harvard Forest in Climate Change Research
Harvard Forest is a leading institution in the study of climate change, serving as both a laboratory and a living canvas for researchers. Since its establishment, scientists have used its diverse ecosystems to monitor and analyze the impacts of climate variation. As one of the most extensively studied forests in the United States, it offers invaluable insights into long-term ecological changes. Through centuries of collected data on temperature and precipitation patterns, researchers can observe, in real-time, the profound effects of climate change on this unique environment.
Moreover, the Harvard Forest serves as an illustrative case for understanding how climate change is reshaping ecosystems. The forest’s scientists engage in numerous research projects that investigate everything from tree species shifts to ecosystem resilience in the face of challenges like invasive pests. For instance, with the ongoing threat of species like the woolly adelgid, the implications of invasive organisms become evident, showing how interconnected and vulnerable forest systems are under climate stress.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of climate change on the ecosystem at Harvard Forest?
The impact of climate change on the Harvard Forest ecosystem is significant, with observable trends including warmer temperatures, milder winters, and changes in tree species compositions. Black birch trees are increasingly replacing dying hemlocks, largely due to the invasive woolly adelgid pest thriving in milder conditions. This shift affects soil chemistry, nutrient flow, and the overall structural dynamics of the forest.
How is Harvard Forest research contributing to understanding climate change?
Harvard Forest research is crucial for understanding climate change through extensive data collection that tracks temperature and precipitation patterns over decades. By analyzing long-term climate trends and conducting a variety of experiments, researchers can observe how climate change affects forest dynamics, including species shifts and ecosystem resilience.
What evidence is there of tree species shift at Harvard Forest due to climate change?
Research at Harvard Forest indicates a clear tree species shift due to climate change, primarily seen in the decline of hemlock trees being replaced by black birches. This change is influenced by warming winters and the spread of invasive pests like the woolly adelgid, which thrive in warmer conditions and affect the ecosystem’s health.
How do invasive pests influence forest dynamics in Harvard Forest?
Invasive pests significantly influence forest dynamics at Harvard Forest, particularly the woolly adelgid, which preys on hemlock trees. As these pests thrive in warmer climates, they contribute to the decline of hemlocks, leading to shifts in species composition and impacting the overall resilience and ecological balance of the forest.
What role does Harvard Forest play in studying ecosystem resilience to climate change?
Harvard Forest plays a pivotal role in studying ecosystem resilience to climate change by providing a living laboratory for long-term ecological research. Scientists monitor ongoing changes and evaluate how different species adapt to the shifting environment, offering insights into potential conservation strategies and the future of forest ecosystems.
What are the long-term climate trends observed at Harvard Forest?
Long-term climate trends observed at Harvard Forest include a general warming and increased precipitation, leading to heavier rainfall events. Data collected since the 1960s reveal significant changes in seasonal weather patterns, such as later winters and altered snowpack, which directly affect forest health and species distribution.
Why is Harvard Forest considered a vital research location for studying climate change?
Harvard Forest is considered vital for studying climate change due to its extensive historical data, diverse research projects, and the unique opportunity to monitor ecological changes in a controlled environment. The forest’s long-term datasets allow researchers to identify trends that are otherwise difficult to discern in shorter timeframes.
How does climate change affect the perceptions of future generations regarding old-growth forests?
Climate change impacts the perceptions of future generations regarding old-growth forests by altering their baseline understanding of what these ecosystems should look like. As climate conditions change, young people may not experience the same forest characteristics, leading to a disconnect in appreciation and conservation efforts.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Impacts | Harvard Forest researchers observe significant ecological changes due to climate change, including alterations in species distribution and forest density. |
| Temperature and Precipitation | Long-term data reveal a warmer and wetter climate, with increased instances of extreme rainfall. |
| Invasive Species | Woolly adelgid is threatening hemlock populations, leading to changes in forest structure and chemistry. |
| Ecosystem Resilience | Despite losses, the forest shows resilience and adaptation, with birch trees gradually replacing hemlocks. |
| Generational Changes | Personal narratives emphasize a shifting baseline where future generations may lack awareness of past forest ecosystems. |
Summary
Climate change at Harvard Forest is a pressing issue that dramatically underscores the urgency for action. The dedicated work of researchers like Emery Boose and Clarisse Hart reveals the profound transformations occurring within this Massachusetts forest as a consequence of climate change. Their observations not only highlight shifts in species and ecosystems but also emphasize the collective emotional investment of the Harvard Forest community in this changing landscape. As the community witnesses the effects of a warming planet in their own backyards, the need for awareness and proactive stewardship becomes increasingly critical.